- What Are Non-Standard Flanges?
- Reasons for Using Non-Standard Flanges
- Common Types of Non-Standard Flanges
- Materials for Non-Standard Flanges
- Manufacturing Process of Non-Standard Flanges
- Applications of Non-Standard Flanges
- Advantages of Non-Standard Flanges
- Challenges with Non-Standard Flanges
- Inspection and Quality Control for Non-Standard Flanges
- Standards and Documentation for Non-Standard Flanges
- How to Order Non-Standard Flanges
- Conclusion
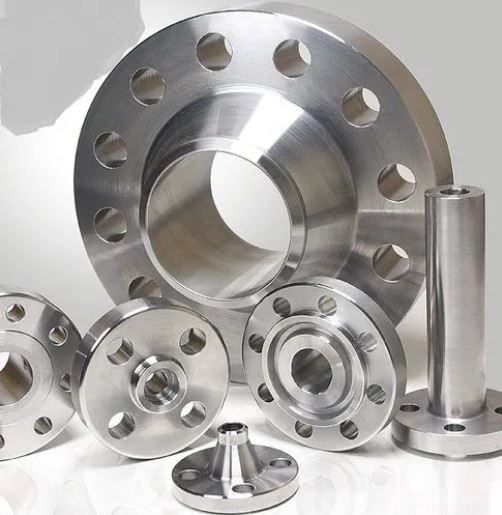
Flanges are critical components used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in industrial piping systems. While most projects utilize standard flanges manufactured according to ASME, EN, JIS, or GOST specifications, there are numerous cases where custom solutions are necessary. These custom-made flanges, known as non-standard flanges, are designed to meet specific project requirements that standard flange dimensions, materials, or pressure ratings cannot fulfill. This article provides a detailed introduction to non-standard flanges, covering their definition, types, manufacturing process, applications, and advantages.
Sunjin Metals Vina (SJM Vina), is a trusted supplier of high-quality steel pipes, flanges, and fittings sourced from South Korea and other countries, fully compliant with international standards.
What Are Non-Standard Flanges?
A non-standard flange is a flange that does not conform to recognized industry standards such as ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1, or JIS B2220. Instead, it is manufactured according to custom dimensions, material specifications, and pressure ratings provided by the customer or project engineer.
Non-standard flanges are often required when:
-
The piping system has unique dimensions.
-
Special materials are needed for extreme environments.
-
Unusual pressure or temperature conditions must be met.
-
The project involves retrofitting into existing non-standard equipment.
Reasons for Using Non-Standard Flanges
1. Custom Dimensions
Certain projects require flanges with unique bolt hole patterns, thicknesses, or diameters not available in standard ranges.
2. Special Materials
Non-standard flanges can be made from exotic alloys such as titanium, duplex stainless steel, or nickel alloys to handle highly corrosive environments or extreme temperatures.
3. Higher Pressure Ratings
When the system’s working pressure exceeds the limits of standard flange ratings, a non-standard design can be engineered for enhanced strength.
4. Space Limitations
Some installations require flanges with reduced dimensions or special shapes to fit into confined spaces.
Common Types of Non-Standard Flanges
Custom Weld Neck Flanges
-
Similar in design to standard weld neck flanges but with dimensions tailored to specific piping layouts or load requirements.
Oversized or Undersized Slip-On Flanges
-
Made with unique bore sizes to fit pipes that do not match standard nominal diameters.
Special Blind Flanges
-
Blind flanges manufactured in irregular shapes or with added features such as inspection ports.
Non-Circular Flanges
-
Oval, square, or rectangular flanges designed for special equipment openings.
Hybrid Design Flanges
-
Flanges that combine features of two standard flange types, such as a lap joint face with a weld neck hub.
Materials for Non-Standard Flanges
The choice of material depends on the service environment, mechanical requirements, and budget. Options include:
-
Carbon Steel: Economical choice for general use.
-
Stainless Steel: For corrosion resistance in chemical and marine environments.
-
Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steel: High strength and superior corrosion resistance.
-
Nickel Alloys (Monel, Inconel, Hastelloy): For extreme chemical and temperature conditions.
-
Titanium: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance in seawater.
Manufacturing Process of Non-Standard Flanges
1. Design and Engineering
The process begins with detailed drawings specifying dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finish requirements.
2. Material Selection
Raw material is chosen based on the application’s pressure, temperature, and corrosion requirements.
3. Forging or Cutting
The flange is produced by forging steel billets or cutting from plate material, depending on size and material type.
4. Machining
Precision machining is carried out to achieve the required bore size, bolt holes, facing type, and surface finish.
5. Heat Treatment
If necessary, heat treatment is applied to improve mechanical properties or relieve internal stresses.
6. Testing and Inspection
Non-standard flanges undergo dimensional inspection, non-destructive testing (NDT), and sometimes pressure testing to ensure compliance with design requirements.
Applications of Non-Standard Flanges
Oil and Gas Industry
Custom flanges for offshore platforms, subsea pipelines, and refinery equipment where conditions exceed standard flange limits.
Chemical Processing
Flanges made from exotic alloys to withstand aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents.
Power Generation
High-pressure, high-temperature flanges for boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers.
Marine and Shipbuilding
Special corrosion-resistant flanges for ship pipelines, ballast systems, and desalination plants.
Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
Non-standard hygienic flanges for specialized processing equipment.
Advantages of Non-Standard Flanges
-
Tailored Fit: Designed to match exact system requirements.
-
Material Flexibility: Wide selection of metals for specific environments.
-
Higher Performance: Can be engineered for higher pressure, temperature, or corrosion resistance.
-
Compatibility: Ideal for retrofitting into existing non-standard systems.
Challenges with Non-Standard Flanges
Longer Lead Times
Custom designs require additional engineering, manufacturing, and inspection time.
Higher Costs
Due to unique specifications, smaller production runs, and specialized materials, non-standard flanges are more expensive than standard options.
Replacement Issues
Since they are custom-made, replacement flanges may require repeating the design and manufacturing process.
Inspection and Quality Control for Non-Standard Flanges
Non-standard flanges undergo rigorous quality control to ensure they meet project specifications:
-
Dimensional Verification: Ensures accurate fit with the mating equipment.
-
Material Certification: Confirms chemical composition and mechanical properties.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Detects surface and internal defects.
-
Hydrostatic or Pneumatic Testing: Validates pressure performance.
SJM Vina maintains strict inspection procedures and provides full traceability to guarantee reliability.
Standards and Documentation for Non-Standard Flanges
Although they do not follow standard dimensions, non-standard flanges can still adhere to relevant industry codes for materials, pressure testing, and manufacturing processes. Common references include ASME, API, ASTM, and ISO specifications.
How to Order Non-Standard Flanges
-
Define Requirements: Provide detailed drawings or specifications including size, pressure rating, material, and facing type.
-
Select Material: Choose the best alloy for the intended service environment.
-
Specify Testing: Decide on inspection methods such as UT, MPI, or hydrostatic testing.
-
Confirm Lead Time: Account for extra production time compared to standard flanges.
Conclusion
Non-standard flanges play a vital role in industrial projects requiring unique dimensions, materials, or performance capabilities. They offer flexibility in design, enhanced performance, and compatibility with specialized systems. However, they also come with challenges such as longer production times and higher costs.
By partnering with experienced manufacturers like Sunjin Metals Vina, customers can ensure that their non-standard flanges are engineered, manufactured, and tested to meet the most demanding specifications, delivering long-term reliability in even the harshest operating conditions. Contact us at +84 33 4233 127 or via email at sjmvina@sunjinmetal.com. Visit www.sjmvina.com.vn for more information and to place your order today!
Số lần xem: 105